Exploring the concept of leaky gut syndrome and its profound impact on health, the article delves into the insights of Dr. Steven Gundry, a renowned heart surgeon and bestselling author. You’ll learn about the primary culprits, like lectins and glyphosate, that Dr. Gundry identifies as causes of this condition and discover methods to measure and manage leaky gut effectively.
Dr. Gundry’s nutritional approach, aimed at preventing disease and improving overall health, is comprehensively covered. From strategies to alleviate autoimmune conditions to a detailed list of foods to avoid, this guide on leaky gut syndrome provides practical steps to promote gut health and enhance longevity. Additionally, discover the top five recommended fruits that are both safe and beneficial to eat, according to Dr. Gundry.

This image is property of i.ytimg.com.
Understanding Leaky Gut Syndrome
Definition of Leaky Gut Syndrome
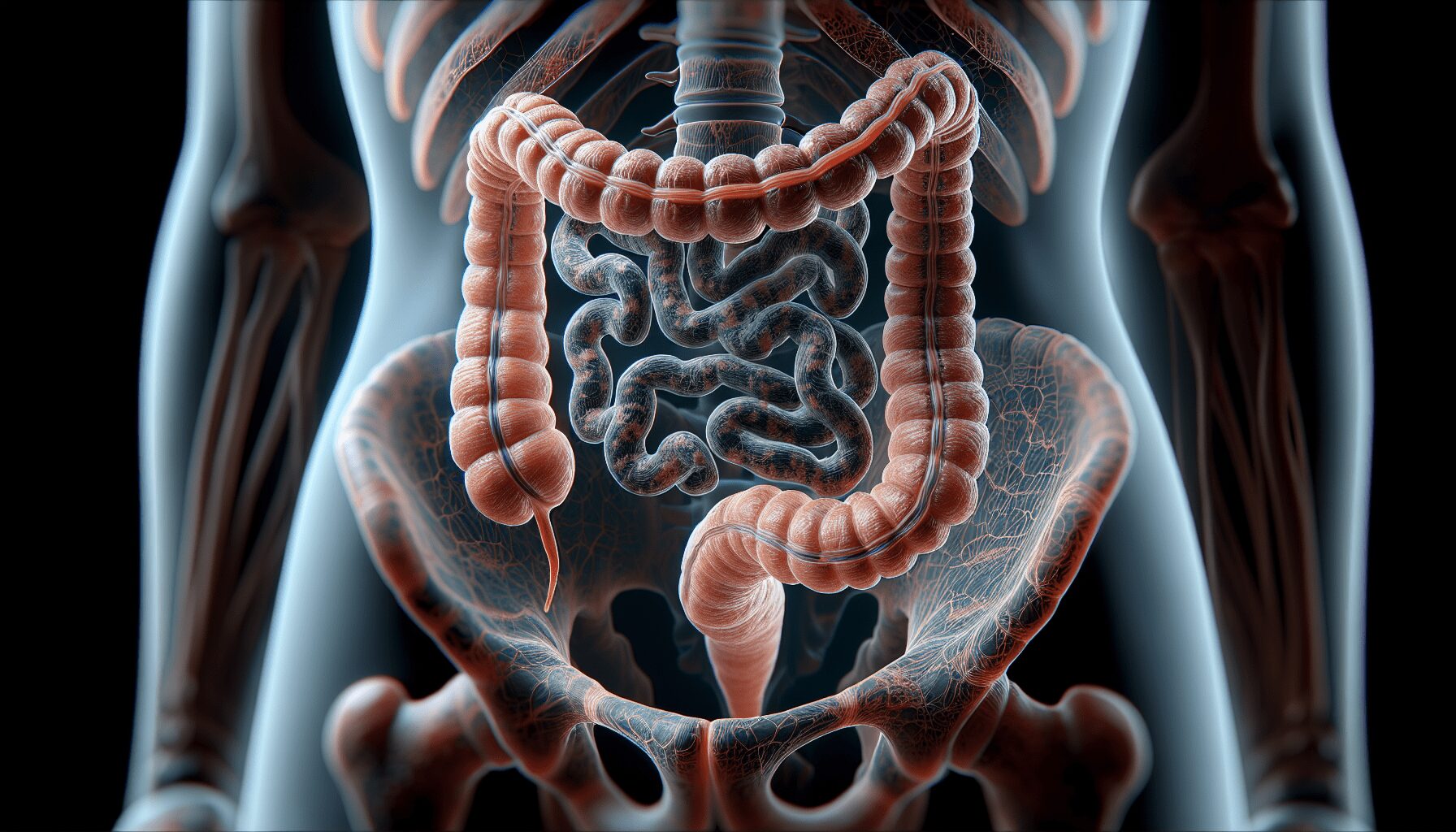
Leaky Gut Syndrome, also known as intestinal permeability, is a condition where the lining of your small intestine gets damaged. This damage causes the lining to become less effective at filtering out harmful substances. Consequently, toxins, microbes, and undigested food particles can “leak” through the intestines and enter the bloodstream. This triggers widespread inflammation and can lead to various health issues. Essentially, the barriers that usually protect your body from unwanted particles weaken, resulting in minor perforations that allow these harmful substances to infiltrate your system.
How the Gut Lining Functions
Your gut lining, or intestinal epithelium, works as a highly selective barrier. Think of it as a finely tuned filter. It’s one cell thick, encompassing an extensive surface area roughly the size of a tennis court. That’s a significant area where nutrients are absorbed, and harmful elements are blocked out. These cells are held together by ‘tight junctions,’ which function like gatekeepers, only allowing beneficial nutrients and waste to pass while blocking harmful substances. This barrier is crucial for maintaining a healthy immune system and metabolic function.
Impacts of a Weakened Gut Lining
When these tight junctions are compromised, it leads to a condition known as leaky gut. This breakdown in the gut lining allows harmful elements like pathogens, toxins, and undigested food particles to enter your bloodstream. The presence of these foreign substances triggers an immune response, causing inflammation and contributing to various health issues. Your body goes into defense mode, which can result in chronic inflammation, digestive problems, autoimmune conditions, and even mental health challenges like anxiety and depression.
The Role of the Gut in Overall Health
Connection Between Gut Health and Disease
Your gut health is inextricably linked to your overall health. The gut microbiome, a community of trillions of bacteria, viruses, and fungi living in your intestines, plays a crucial role in nutrient absorption, digestion, and immune function. Poor gut health is associated with various chronic conditions, including diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and gastrointestinal disorders like IBS. Emerging research increasingly supports the notion that many diseases originate in the gut, pointing to the gut as a central player in maintaining overall health.
Gut Health and Autoimmune Conditions
Autoimmune diseases occur when your immune system mistakenly attacks your body’s tissues. Conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, and lupus have shown strong links to gut health. The theory is that a leaky gut allows for the passage of bacterial toxins and other foreign substances into the bloodstream, which the immune system then attacks. Over time, this can cause the immune system to begin attacking your body’s tissues, mistakenly identifying them as harmful invaders.
Impact on Mental Health and Cognitive Function
The gut-brain axis signifies the profound connection between your gut and mental health. A healthy gut can positively affect brain function and mood, while a compromised gut can contribute to mental health issues. Conditions like depression, anxiety, and even cognitive declines such as dementia have been linked to gut health. This is because the gut microbiome produces neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which are critical for mood regulation and cognitive function.
Causes of Leaky Gut Syndrome
Role of Lectins
Lectins are a type of protein found in various plants that serve as a defense mechanism against pests. However, when consumed in significant amounts, lectins can bind to the gut lining, causing damage and increasing permeability. Foods high in lectins include beans, lentils, and certain vegetables. Dr. Gundry emphasizes the importance of reducing lectin intake to maintain gut health and prevent the cascading effects that contribute to leaky gut syndrome.
Impact of Glyphosate on Gut Health
Glyphosate is a herbicide commonly used in agricultural practices, and its pervasive use means it is often present in many foods. This chemical can disrupt the gut microbiome and has been shown to increase gut permeability. As an antibiotic, glyphosate kills beneficial bacteria, creating an imbalance that can harm the gut lining. This disruption can pave the way for leaky gut syndrome and its related health complications.
Other Potential Causes
Beyond lectins and glyphosate, numerous other factors could contribute to a leaky gut. Chronic stress is a significant one, as it leads to increased levels of the hormone cortisol, which can weaken the gut lining over time. Poor diet, rich in processed foods and sugars, can also harm the gut microbiome. Lastly, chronic use of NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) like ibuprofen can damage the gut lining, making it more permeable.
Dr. Steven Gundry’s Insights
Background on Dr. Steven Gundry
Dr. Steven Gundry is a renowned heart surgeon who has transitioned to focusing on nutritional approaches to prevent the surgery he used to perform. With a career spanning over 10,000 successful heart surgeries and numerous medical device patents, Dr. Gundry’s medical background is impressive. His shift towards nutrition-based preventative care is rooted in his belief that many chronic diseases stem from poor dietary choices.
Key Principles in His Teachings
Dr. Gundry’s teachings emphasize the importance of understanding what you put into your body. He advocates for a diet low in lectins and glyphosate, focusing instead on natural, minimally processed foods that support gut health. His key principles revolve around avoiding harmful food components like gluten, lectins, and added sugars, while incorporating foods with prebiotic fibers and beneficial nutrients that promote a healthy gut microbiome.
Gundry’s Focus on Nutrition Over Surgery
Dr. Gundry’s approach marks a significant shift from surgical intervention to nutritional empowerment. By prioritizing dietary modifications, he believes that individuals can prevent many of the chronic illnesses that often require surgical solutions. His motto could be summarized as “better health through better diet,” encouraging people to take control of their health by making informed dietary choices.

Measuring Leaky Gut Syndrome
Available Blood Tests
Quantifying leaky gut syndrome can be effectively done through various blood tests. Common tests include anti-zonulin, anti-actin, and anti-LPS IgG. These tests measure the presence of antibodies that indicate increased gut permeability. They help gauge how sensitive your body is to the factors that typically cause gut lining deterioration.
Indicators of Gut Permeability
Indicators of gut permeability include elevated levels of zonulin, a protein that modulates the tight junctions between gut epithelial cells. Higher levels of zonulin in your blood suggest that your tight junctions are loosening, allowing for gut permeability. Other markers include antibodies against endotoxins like lipopolysaccharides (LPS), which are present in the outer membrane of certain bacteria.
Interpreting Test Results
Interpreting these test results involves understanding what elevated levels signify for your health. High levels of zonulin or LPS antibodies may indicate that your gut lining has been compromised, leading to leaky gut syndrome. This can translate to various health challenges, from digestive issues to autoimmune conditions. Understanding these results can guide you and your healthcare provider in tailoring a management plan to restore gut health.
Managing and Reversing Leaky Gut Syndrome
Dietary Modifications
Dietary changes are fundamental in managing and reversing leaky gut syndrome. Focus on eliminating or significantly reducing foods high in lectins and glyphosate. Incorporate whole foods rich in nutrients, while avoiding processed foods. Probiotic and prebiotic-rich foods can also aid in strengthening your gut lining, making it less permeable over time.
Role of Prebiotic Fiber
Prebiotic fibers are non-digestible fibers that serve as food for beneficial gut bacteria. Incorporating foods like Jerusalem artichokes, tiger nuts, and Belgian endive into your diet can bolster your gut flora. These beneficial bacteria produce short-chain fatty acids that reinforce the integrity of the gut lining, making it less permeable and more resilient to harmful substances.
Lifestyle Changes to Support Gut Health
In addition to dietary modifications, lifestyle changes can make a significant impact. Regular exercise helps regulate inflammation and maintain a healthy gut. Stress management techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can lower cortisol levels, reducing the strain on your gut lining. Adequate sleep and hydration are also essential in maintaining gut health.
Foods to Avoid for Gut Health
Significance of Avoiding Lectin-Rich Foods
Lectins can be problematic because they bind to the gut lining and can cause inflammation and permeability. By avoiding or preparing lectin-rich foods properly, such as by soaking or pressure cooking beans and legumes, you reduce the risk of damaging your gut lining. Dr. Gundry advises minimizing the intake of foods high in lectins to prevent these adverse effects.
Why Certain Grains Are Detrimental
Grains, especially those containing gluten, can cause inflammation and contribute to leaky gut. They contain lectins and can interfere with the gut’s ability to absorb nutrients properly. By opting for gluten-free grains like millet and sorghum, you can still enjoy grains without compromising your gut health.
Impact of Nightshades and Beans
Nightshades such as tomatoes, potatoes, and eggplants contain lectins that may contribute to gut permeability. While these can be a healthy part of many diets, if you have a sensitive gut or are experiencing symptoms of leaky gut syndrome, you may want to minimize or eliminate these foods. Proper preparation methods like peeling, de-seeding, and pressure cooking can reduce their lectin content.
Top 5 Foods to Avoid
Beans and Legumes
Beans and legumes are high in lectins, making them a common culprit in contributing to a leaky gut. If you need to consume them, ensure they are properly soaked and pressure-cooked to reduce their lectin content. However, minimizing their intake altogether may be even more beneficial for your gut health.
Grains
Grains, particularly those containing gluten, should be limited. These grains are relatively new additions to the human diet and can disrupt the integrity of your gut lining due to their lectin content. Opt for healthier alternatives like millet, sorghum, and other gluten-free grains.
Nightshades
Nightshades like tomatoes, potatoes, and eggplants contain lectins that can exacerbate gut issues. If you decide to eat nightshades, prepare them by peeling and de-seeding, or use pressure cooking methods to reduce their harmful components.
Certain Fruits
High-sugar fruits, especially those out of season, should be avoided as they can disrupt the balance of your gut microbiome. Stick to low-sugar, seasonal fruits that are less likely to harm your gut health.
Squash
Squash and other similar vegetables contain lectins and should be consumed cautiously. Proper preparation methods like peeling and de-seeding can help mitigate their lectin content if you choose to include them in your diet.
Recommended Fruits for Gut Health
Benefits of Low-Sugar Fruits
Low-sugar fruits are beneficial for your gut because they provide essential nutrients without contributing to spiking blood sugar levels or feeding harmful gut bacteria. These fruits help maintain a balanced gut microbiome and support overall gut health.
Top Recommended Berries
Berries like raspberries, blackberries, and wild blueberries are low in sugar and high in polyphenols, compounds that have been shown to support gut health. These fruits are rich in antioxidants and fiber, making them an excellent choice for maintaining a healthy gut.
Noteworthy Fruits: Avocado, Kiwi, and More
Avocados are nutrient-dense and packed with healthy fats that support gut health. Kiwi, especially when eaten with the skin, provides a good source of fiber. Pomegranate seeds are also beneficial due to their high polyphenol content. Incorporating these fruits into your diet can significantly benefit your gut health.
Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
Leaky gut syndrome is a condition wherein the gut lining becomes permeable, allowing harmful substances to enter the bloodstream. This can result in widespread inflammation and contribute to a range of health issues, including autoimmune conditions and mental health challenges. Key causes include lectins, glyphosate, and other dietary and lifestyle factors.
Importance of Gut Health for Longevity
Maintaining a healthy gut is crucial for preventing chronic diseases and promoting overall well-being. It is the foundation for good health, affecting everything from digestion and immune function to mental health and cognitive performance.
Encouragement to Follow Dr. Gundry’s Guidelines
Dr. Steven Gundry’s teachings highlight the importance of understanding and managing your diet to maintain a healthy gut. By following his guidelines, which include avoiding harmful foods and incorporating beneficial ones, you can take proactive steps towards improving your health and longevity. Make the necessary dietary and lifestyle changes today to ensure a healthier tomorrow.